It is one of the most discussed diets in recent years, severely discouraged by some, but of proven effectiveness in weight reduction, even by people who had failed to lose weight in any other way. The ketogenic diet is based on the induction of a biochemical state called ketosis in which the body, after having consumed the available sugar, begins to metabolize the stored fats. The principle, in itself, is physiological, but it is not suitable for everyone and cannot be followed as a do-it-yourself regime.
The mechanism itself is simple: our body uses the energy from glycides, such as sugar and carbohydrates, present in the blood, for its daily activities, such as movement, breathing and the preservation of body temperature. To force it to affect the stocks stored in the form of fat, it is necessary to eliminate (or reduce to very small quantities) the amount of glycides coming from the diet. At some point our body realizes that it has “run out of fuel”; some organs and tissues begin to use fatty acids as an energy source: the brain, the nervous system and some muscle fibers, on the other hand, produce ketone bodies, which are obtained by metabolizing lipid stocks. The body thus enters a biochemical state called ketosis, in which in practice the physical uses fats to produce energy, given the shortage of available sugars.
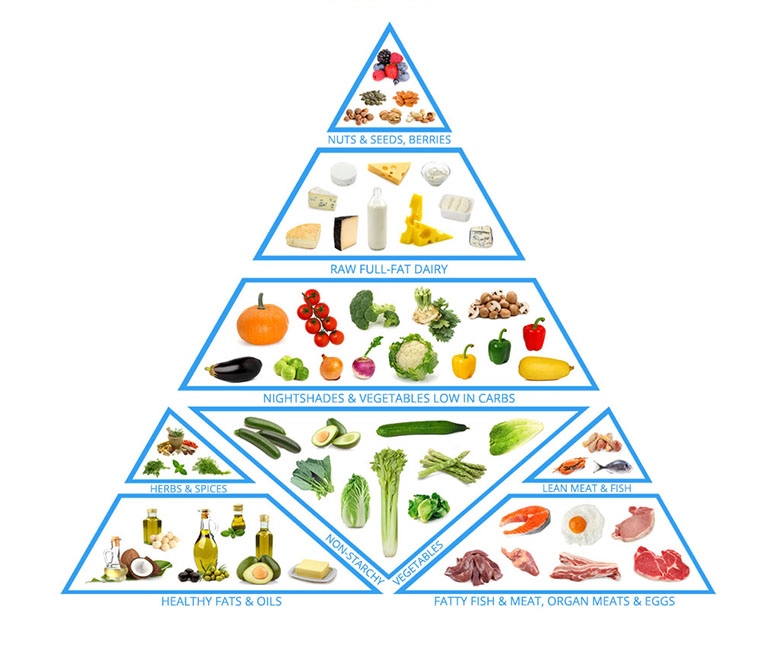
The state of ketosis is not easy to reach and maintain: it is necessary to eliminate all the sources of glucose from the diet, including bread and pasta, sugar, alcohol, potatoes, but also fruit, milk and dairy products, legumes and red / orange vegetables like tomatoes and carrots, usually also allowed in low-calorie regimens. Proteins can be taken freely in the form of meat, fish, eggs: it is often advisable to complete the diet with protein supplements and salts, vitamins and omega 3, given the reduced contribution from the table. It is also essential to drink plenty of water, at least two liters a day.
After a couple of days of ketosis, weight loss begins to occur, rather quickly and consistently. Since the state of ketosis is linked to the level of blood glucose in the blood, it goes without saying that every deviation is paid for with the loss of this complex biochemical balance: just a small fruit, or a drink or a piece of bread is enough to compromise the ketosis and negate all efforts: the physicist will in fact recognize the presence of glucose and will resume using it. For this reason, when the desired weight is reached, it is necessary to reintroduce the normal foods very gradually so as not to recover the pounds in a short time.
The ketogenic diet it is unsuitable for those suffering from kidney diseases and it is necessary, during the diet and in the subsequent maintenance period.
If done correctly and with the use of the appropriate supplements, the diet will simply be protein, and not high protein; even maintaining the weight achieved will be simpler and more durable. On the other hand, the ketogenic diet makes it possible to dispose of a considerable number of kilos in a short time and, if followed correctly, makes it possible to lose weight significantly, reducing only the fat mass, without affecting the lean muscle mass.